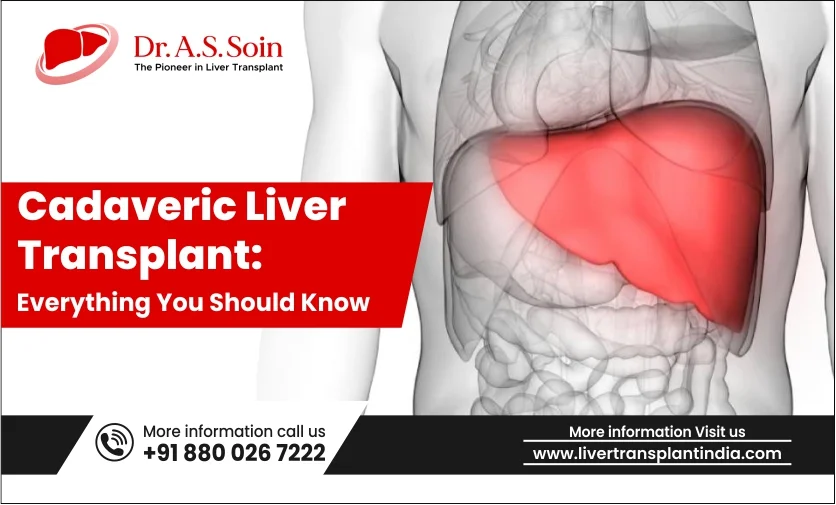
A cadaveric liver transplant, also known as a deceased donor liver transplant, is a critical medical procedure used to treat acute liver failure or end-stage liver disease. This intricate surgery involves replacing a failing liver with a healthy one from a deceased donor. For a successful transplant, blood type and size must align, whereas immunological compatibility is mostly not required for liver transplants. Cadaveric liver transplants offer a significant chance for improved survival and quality of life for patients suffering from severe liver disease, especially in families where a live liver donor is not there or where liver donation can’t be done due to many graft-recipient factors. Despite its complexities, this surgery marks a transformative milestone in modern medicine, underscoring the vital role of organ donation in life preservation.
Table of Contents
ToggleEligibility Criteria for Cadaveric Liver Transplant
Eligibility for a cadaveric liver transplant is determined by several factors, including the severity of liver disease, overall health, and the potential for recovery. Here are the key criteria:
- Severity of Liver Disease: Transplants are typically reserved for individuals with acute liver failure or end-stage liver disease that cannot be managed through other medical treatments.
- Absence of Contraindications: Candidates should not have conditions that significantly increase surgical risk or reduce the likelihood of a successful outcome.
- General Health Status: A comprehensive medical evaluation is necessary to ensure candidates are fit for surgery.
- Liver Function: Severe impairment of liver function, as indicated by laboratory tests, imaging studies, and biopsy results, is essential.
- Medical Urgency: Priority is given to individuals with the most critical medical needs, considering the severity, symptoms, and prognosis of liver disease.
- Surgical Tolerance: Candidates must be stable enough to withstand surgery and the recovery period.
- Adherence to Medical Recommendations: Candidates must demonstrate the ability to comply with lifestyle changes, medication regimens, and follow-up care.
- Age Consideration: While age is a factor, it is not a strict determinant; suitability is assessed based on overall health and potential benefit from the transplant.
- Multidisciplinary Assessment: A team of hepatologists, transplant surgeons, coordinators, social workers, and other specialists evaluates eligibility.
- Psychosocial Evaluation: This assessment determines mental and emotional preparedness, support systems, and the ability to manage the challenges of the transplant process.
Pre-Transplant Diagnostics
Before a cadaveric liver transplant, several assessments are performed:
- Evaluation of Liver Disease: Detailed analysis of the underlying liver condition, including its severity and impact on liver function.
- Liver Function Tests: Laboratory tests such as blood bilirubin, albumin, prothrombin time, and liver enzyme levels.
- Imaging Studies: Radiological examinations like liver biopsy, CT scan, MRI, and ultrasound to assess liver damage and anatomy.
- Cardiac Evaluation: Assessment of cardiovascular risk factors and heart function to ensure suitability for anaesthesia and surgery.
- Pulmonary Function Tests: Evaluation of lung function to detect any respiratory issues that might affect surgery outcomes.
- Cancer Screening: Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and other liver-related cancers.
- Infectious Disease Tests: Screening for infections such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, and other viral or bacterial infections to minimize post-transplant complications.
- Nutritional Assessment: Analysis of dietary habits and nutritional status to optimize support before and during surgery.
- Psychosocial Assessment: Evaluation of mental health, social support, coping mechanisms, and adherence to medical guidelines.
- Multidisciplinary Transplant Evaluation: A comprehensive review by a team of healthcare professionals to determine eligibility and assess the procedure’s risks and benefits.
The procedure of Cadaveric Liver Transplant
The process involves several steps:
- Donor Selection: Identifying a suitable deceased donor whose liver matches the recipient’s blood type, size.
- Organ Retrieval: Surgical extraction of the liver from the deceased donor while maintaining its viability.
- Organ Preservation: Using techniques like cold perfusion or hypothermic machine perfusion to preserve the liver for transport.
- Recipient Preparation: Optimizing the patient’s health pre-surgery, addressing coexisting conditions, and ensuring readiness for surgery.
- Anesthesia and Incision: Administering anaesthesia and making an incision in the upper abdomen to access the native liver.
- Hepatectomy: Removing the diseased liver, either partially or totally, depending on the recipient’s anatomy and liver condition.
- Graft Implantation: Attaching the donor liver’s hepatic artery, portal vein, and hepatic vein to the recipient’s blood vessels.
- Biliary Reconstruction: Connecting the donor liver’s bile ducts to the recipient’s bile ducts or establishing a biliary-enteric anastomosis for bile drainage.
- Hemostasis and Closure: Ensuring hemostasis and closing the surgical incision with sutures or staples.
- Postoperative Care: Providing intensive care and monitoring to prevent complications, optimize graft function, and support recovery.
Post-Transplant Recovery
Recovery involves several phases:
- Hospital Stay: Patients typically stay in the hospital for one to two weeks to ensure graft function and monitor for complications.
- Immunosuppressive Therapy: Lifelong immunosuppressive medication is required to prevent graft rejection, with careful monitoring to balance side effects and rejection prevention.
- Regular Follow-Up: Frequent visits to the transplant team to monitor liver function, drug levels, and overall health.
- Physical Rehabilitation: Gradual increase in physical activity and therapy under guidance to regain strength and mobility.
- Dietary Guidelines: Adopting a balanced diet low in saturated fats and sodium to support liver health and prevent complications like dyslipidemia and hypertension.
- Infection Prevention: Maintaining hygiene, avoiding exposure to illness, and staying up-to-date with vaccinations.
- Psychological Support: Accessing counselling services, support groups, or mental health providers to manage the emotional aspects of transplantation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Following recommended changes such as regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding alcohol, tobacco, and harmful drugs.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Lifelong medical check-ups and tests to detect and manage issues like infections, graft rejection, and new cancers.
- Adherence to Medical Regimen: Strict compliance with medication schedules, follow-up appointments, and lifestyle recommendations is essential for long-term success and graft preservation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long is the waiting period for a cadaveric liver transplant?
The waiting period varies based on factors like blood type, disease severity, and donor organ availability, ranging from weeks to months or longer.
What determines eligibility for cadaveric liver transplant surgery?
Eligibility is based on liver disease severity, overall health, absence of active infections or cancer, and adherence to medical recommendations.
What are the risks or side effects of cadaveric liver transplant surgery?
Risks include infection, organ rejection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anaesthesia or medications, though advancements in techniques have reduced these risks significantly.
What is the recovery timeline after cadaveric liver transplant surgery?
Recovery times vary, with most patients spending several weeks in the hospital followed by outpatient rehabilitation. Full recovery and return to normal activities may take up to a year.