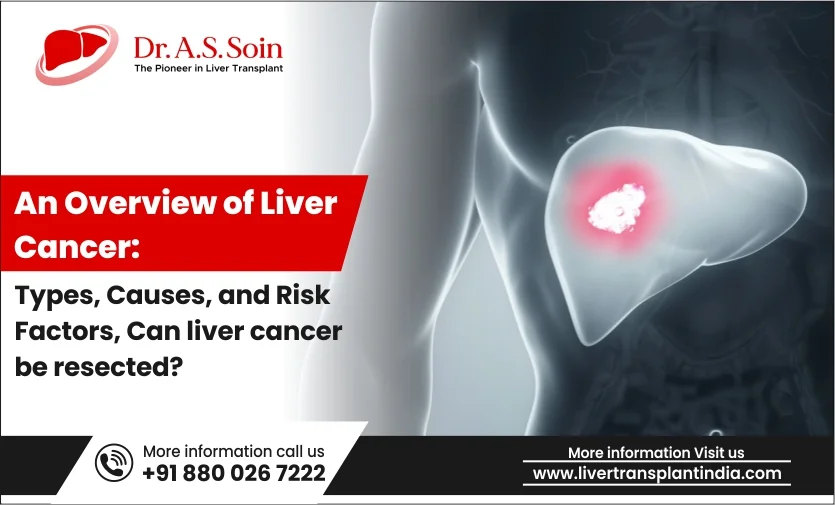
Liver cancer poses a significant global health challenge, underscoring the importance of understanding its diverse types, causes, and risk factors. By exploring these aspects, we can better grasp the complexities of this condition and optimize strategies for prevention and treatment. Consulting with leading liver cancer specialists ensures access to expert diagnosis and management.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Liver Cancer
Liver cancer, or hepatic cancer, refers to the abnormal proliferation of cells within the liver, a vital organ responsible for metabolic functions, detoxification, and protein synthesis. Its prevalence varies globally, often correlating with regions where chronic liver diseases prevail.
The liver’s anatomy, including its lobes, vascular supply, and bile duct system, is fundamental to comprehending how cancer develops within this organ.
Types of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer manifests in several distinct forms, each presenting unique challenges and treatment considerations.
- Primary Liver Cancer :- Primary liver cancer encompasses two main types:
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): The most prevalent form, originating from hepatocytes, the primary liver cells.
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Arising from the bile ducts within the liver, this less common type requires specialized clinical management.
- Secondary Liver Cancer :- Secondary liver cancer involves metastatic tumors originating from primary sites like the colon or breast, which spread to the liver.
Causes of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer can stem from various underlying conditions and risk factors:
- Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Hepatitis B and C infections significantly elevate long-term liver cancer risks.
- Alcohol-Related Liver Disease: Prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption leading to cirrhosis increases susceptibility.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Linked to obesity and metabolic syndrome, NAFLD may progress to liver cancer in severe cases.
- Genetic Factors: Conditions such as hemochromatosis and inherited metabolic disorders heighten vulnerability.
- Environmental Toxins: Exposure to aflatoxins in contaminated foods and industrial chemicals contributes to cancer development.
Risk Factors for Liver Cancer
Several factors influence individual susceptibility to liver cancer:
- Age and Gender: Incidence increases with age, with men typically more affected than women.
- Chronic Liver Diseases: Cirrhosis, whether due to viral hepatitis, alcohol, or other causes, significantly heightens risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, obesity, physical inactivity, and smoking contribute to increased risk.
- Geographic and Ethnic Variations: Higher rates in Asia and Africa are linked to endemic hepatitis B and environmental factors.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer commonly presents with:
- Abdominal Pain: Persistent discomfort in the upper abdomen, sometimes radiating to the back or shoulder.
- Swelling: Abdominal swelling or a palpable lump under the ribs.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden weight loss despite normal eating habits.
- Loss of Appetite and Fatigue: Reduced hunger leading to weight loss, accompanied by persistent tiredness.
Diagnosis of Liver Cancer Diagnosis involves
- Medical History and Physical Examination
- Blood Tests
- Imaging Techniques
- Biopsy for definitive cancer type and staging.
Stages of Liver Cancer
Stages range from localized tumors (Stage 1) to extensive metastasis (Stage 4), guiding treatment decisions and prognostic assessments.
Can Liver Cancer Be Resected?
Liver resection removes cancerous liver segments, contingent on tumor size, location, and liver function. Success hinges on pre-operative evaluation, surgical precision, and post-operative care.
Treatment of Liver Cancer
Treatment options include:
- Surgical Interventions: Hepatectomy and liver transplantation for localized and advanced cases, respectively.
- Ablation Therapy: Radiofrequency or microwave techniques for localized tumors.
- Non-Surgical Treatments: TACE, radioembolization, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy for advanced stages or inoperable cases.
- Palliative Care: Symptom management and supportive therapies for advanced disease.
Multidisciplinary Approach Effective liver cancer treatment involves collaboration among oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and support specialists to tailor care to individual needs.
Prevention and Prognosis Preventive measures include vaccination against hepatitis B, lifestyle adjustments, and early detection through regular screening. Prognosis varies based on timely intervention and treatment response.
Recovery and Follow-Up Post-treatment care emphasizes surveillance for recurrence, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support to enhance recovery and quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding liver cancer’s complexities empowers proactive health decisions. Increased awareness and early intervention are crucial in mitigating its impact globally.
For consultations on liver cancer, contact Liver Transplant India for comprehensive care under leading specialists.