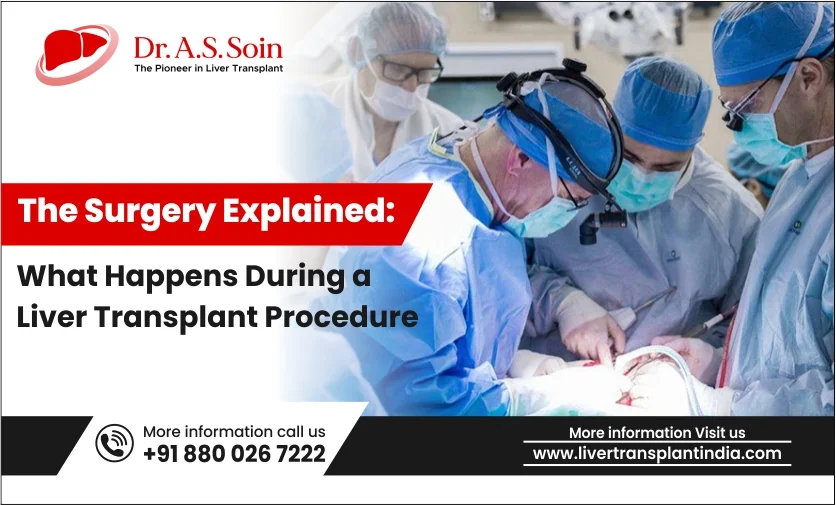
For individuals suffering from severe liver diseases, liver transplant surgery is a life-saving procedure that offers renewed hope. The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous critical functions, including aiding in digestion and detoxifying the blood. When the liver is severely damaged by conditions such as cirrhosis or acute liver failure, a transplant becomes the only viable option to restore health and improve quality of life.
This article provides a detailed, step-by-step explanation of the liver transplant process, from pre-operative preparation to post-operative recovery, to help you understand how this complex procedure is performed.
Table of Contents
TogglePre-Operative Preparation
Patient Evaluation Before undergoing liver transplant surgery, a thorough evaluation is crucial to ensure the patient is a suitable candidate. Key steps include:
- Medical Assessments: The patient undergoes comprehensive tests, including liver function tests, blood work, and overall health assessments. These tests identify any potential complications and determine the patient’s eligibility for a transplant.
- Imaging Studies: Advanced imaging techniques such as ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs provide detailed views of the liver and surrounding organs. These images help the surgical team assess the liver’s condition and plan the procedure.
- Psychological Readiness: Psychological preparation is equally important. Patients often meet with a mental health professional to discuss the emotional and psychological impacts of the surgery. This support helps manage anxiety and prepares patients mentally for the procedure.
Donor Coordination & Organ Matching: For the organ compatibility as far as liver is concerned only a blood group match is required which makes it an easy start and ofcourse further investigations are needed to acertain the liver graft quality and acceptable anatomy. Liver transplant can also be done in case of blood group incompatible pairs aswell, for which the liver transplant surgeon/team has to evaluate the recipient in detail, clinically and specific blood antibodies levels for further planning.
Once a suitable donor liver is identified, the surgical team coordinates the timing and logistics of the transplant.
Surgical Preparation Several important steps are taken to prepare the patient for surgery:
- Fasting: Patients must fast for a specified period before surgery to ensure an empty stomach, reducing the risk of complications during the procedure.
- Medication Management: The medical team provides specific instructions regarding which medications should be taken or avoided before surgery. This may include starting new medications or adjusting current ones to prepare the body for the procedure.
- Pre-Surgery Instructions: Patients receive detailed guidelines on what to bring, when to arrive at the hospital, and how to prepare for surgery on the day of the operation, ensuring a smooth transition from the pre-operative phase to the surgical procedure.
The Surgical Procedure
The liver transplant procedure begins with anesthesia, followed by a series of carefully coordinated steps:
Anesthesia and Incision The patient is placed under general anesthesia, ensuring they remain unconscious and pain-free throughout the surgery. The surgical team then makes an incision on the abdomen, allowing access to the liver and surrounding organs. In some cases, a “bilateral subcostal incision,” involving two incisions along the lower ribs, may be used.
Removing the Diseased Liver The next step involves carefully removing the diseased liver:
- Detachment: Surgeons detach the liver from surrounding structures, including severing the blood supply and bile ducts while preserving these vessels for reconstruction during implantation. Precision is vital to avoid bleeding and damage to nearby organs.
- Extraction: The diseased liver is then carefully removed from the abdominal cavity. During this process, the surgical team takes extra care to prevent bleeding and maintain stable vital signs.
Implanting the New Liver Once the diseased liver is removed, the new liver is prepared for implantation:
- Insertion: The healthy liver is gently placed into the abdomen, aligned correctly in its anatomical position.
- Vascular Connection: Surgeons connect the blood vessels of the new liver to the patient’s existing blood vessels, restoring blood flow and enabling the liver to function.
- Bile Duct Connection: The bile ducts of the new liver are connected either to the patient’s existing bile ducts or an external bile drainage system, ensuring proper bile flow, essential for digestion.
Closure and Observation The final steps involve closing the incision and monitoring the patient in the initial recovery phase:
- Closure: The surgical team closes the incision using sutures or staples, carefully inspecting the abdominal cavity for any signs of bleeding or complications before completing the closure.
- Post-Surgery Monitoring: The patient is moved to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) for close observation. ICU staff monitor vital signs, manage pain, prevent infections, and ensure the new liver begins functioning properly. This early stage is critical as the body adapts to the new liver and any potential complications are promptly addressed.
Post-Surgery Care
Immediate Recovery The focus shifts to immediate recovery after the liver transplant surgery. Typically a reciepient spends a few days in ICU where he is extubated and stabilised before shifting to ward room.
- Monitoring: Regular blood tests are conducted to monitor liver function and detect any early signs of complications. Monitoring also includes checking for signs of bleeding, infection, or liver rejection.
- Initial Recovery: Patients begin the recovery process by waking up, eating, drinking, and gradually increasing physical activity. Starting with basic tasks like sitting up in bed, patients progress to assisted walking, which aids healing and helps prevent complications such as lung infections and blood clots.
Long-Term Care Long-term care is vital to the success of a liver transplant:
- Medication: Patients must take immunosuppressive medications to prevent the body from rejecting the new liver. These medications must be taken regularly and as prescribed. Additional medications may include antibiotics to prevent infection and drugs to manage side effects.
- Lifestyle Changes: Patients are advised to adopt a healthy lifestyle, including avoiding alcohol and tobacco, following a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity. Nutritionists and physical therapists provide guidance to support liver function and overall health.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with the transplant team are essential to monitor liver function and overall health. These visits typically involve physical exams, imaging studies, and blood tests to ensure the liver is functioning well and to detect any potential issues early.
World-Class Liver Transplant Care with Dr. A.S. Soin
For unparalleled expertise in liver transplantation, trust the Liver Transplant India team at Medanta – The Medicity, Gurgaon, led by Dr. A.S. Soin. Dr. Soin is a global pioneer in liver transplantation and has revolutionized the practice in India and worldwide.
The team at Medanta utilizes state-of-the-art facilities and innovative techniques for living donors, cadaveric donors, and pediatric liver transplants to deliver exceptional care and successful outcomes.
In addition to personalized care, Dr. Soin and his colleagues have a proven track record of successfully completing complex liver procedures. The Liver Transplant India team at Medanta – The Medicity stands out for their cutting-edge therapies, comprehensive care, and dedication to liver health.
Whether seeking advanced liver treatment or a consultation with a specialist, Dr. Soin’s team is committed to providing exceptional care with a focus on patient comfort and successful outcomes.
Final Thoughts
The liver transplant process involves three critical phases: pre-operative preparation, surgery, and post-operative care. The process includes matching and preparing the liver, evaluating patients, removing the damaged liver, and implanting the new one. Post-surgery recovery focuses on pain management and monitoring for complications.
Understanding these phases is essential for patients and their families to set realistic expectations and prepare for the journey ahead. Knowing what to expect at each stage can make the overall experience more manageable and contribute to a smoother recovery.